- Leadership Prep School Frisco
- Special Programs
- Special Education
District Resources
Page Navigation
Special Education
-
Leadership Prep School provides special education services for students with disabilities who have a need for specially designed instruction. We are actively involved with efforts to ensure that children with learning challenges have access to evaluations and services, when appropriate. Parents who have concerns about their child's development or academic performance may contact Lensie Walker, Special Education Coordinator, or your campus principal for more information. Services are available for children who meet the eligibility criteria in one of the following areas: auditory impairment, autism, emotional disturbance, learning disability, intellectual disability, orthopedic impairment, other health impairment, speech/language impairment, traumatic brain injury or visual impairment.
The Special Education Information Center (SPEDTex) provides resources and interactive features for increasing family awareness of disabilities and special education processes, with the goal of improving partnerships between schools and families.
Contact information
Phone: 1-855-773-3839
Email: inquire@spedtex.org
Live Chat: https://www.spedtex.org/
-
Special Education Referral
At any time, a parent may request an evaluation for special education services by contacting the campus and requesting that the request be considered by the Student Success Team (SST) or the Section 504 Committee if the student is protected under Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973. If the SST or 504 Committee recommends a special education evaluation, Leadership Prep School must decide if the evaluation is needed within a reasonable period of time. If the evaluation is needed, the parent will be notified and offered an opportunity to provide informed written consent for the evaluation no later than the 15th school day after the written request for evaluation is made.
Leadership Prep must complete the evaluation and the written report within 45 school days from the date LPS received the written consent. LPS will provide a copy of the evaluation report to the parent.
LPS will not use intervention strategies, including multi-tiered systems of support, to delay or deny the provision of a full and individual evaluation of a child suspected of having a specific learning disability, including dyslexia or a related disorder.
If an evaluation is not warranted, LPS will provide the parent with prior written notice which explains why the student will not be evaluated. This written notice will include a statement that informs parents of their rights; in addition, LPS will provide parents a copy of the Notice of Procedural Safeguards. Additional information regarding IDEA is available in a companion document, Parent’s Guide to the Admission, Review, and Dismissal Process.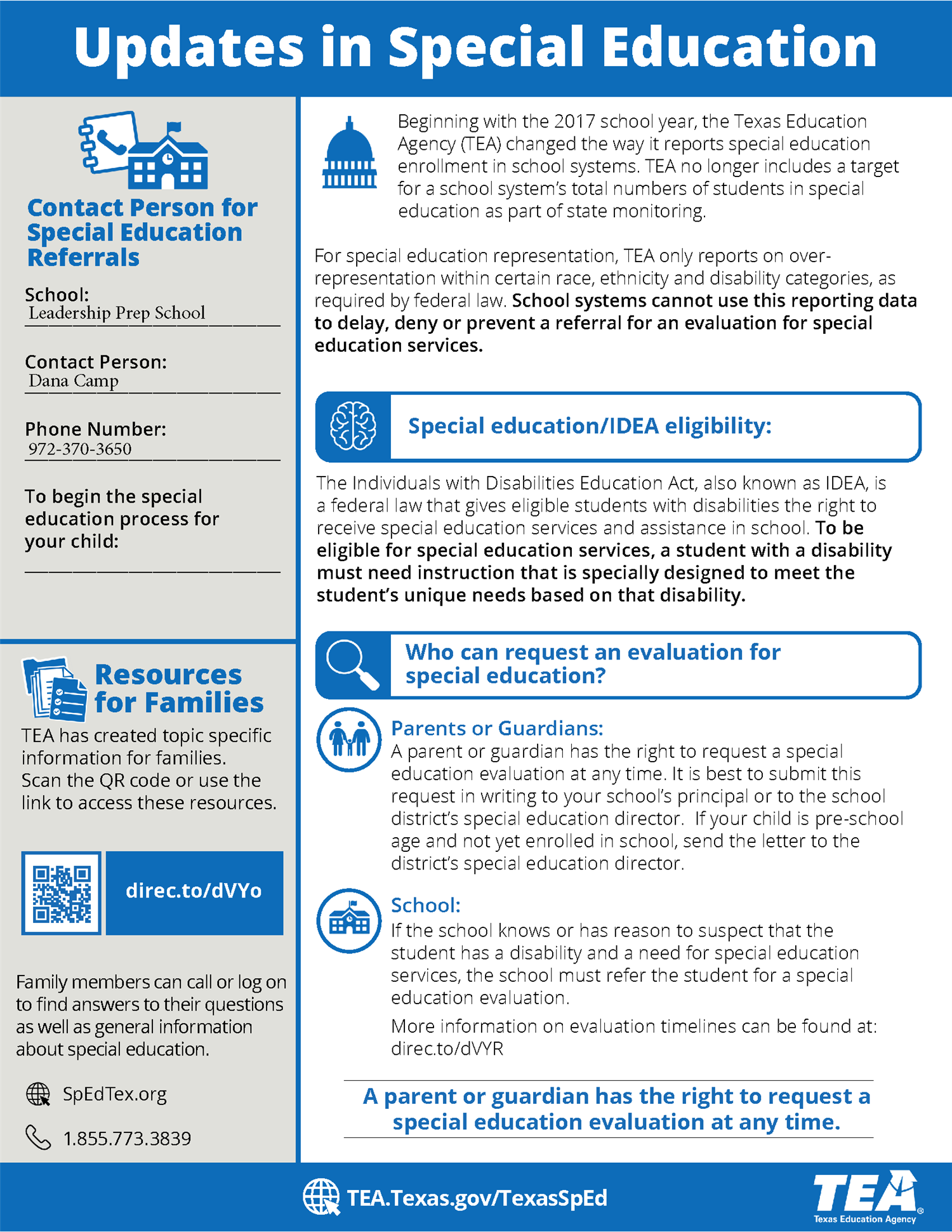
-
Eligibility
The TEA's Parent's Guide to the Admission, Review & Dismissal Process states: There is a two-part test for determining whether your child is eligible for special education and related services: (1) your child must have a disability; and (2) as a result of the disability, your child must need special education and related services to benefit from education. To meet the first part of the two-part test for eligibility, a child between the ages of 3 through 21, except as noted, must meet the criteria for one or more of the disability categories listed below:
- auditory impairment (from birth);
- autism;
- deaf-blindness (from birth);
- emotional disturbance;
- intellectual disability;
- multiple disabilities;
- noncategorical early childhood (ages three through five);
- orthopedic impairment;
- other health impairment;
- specific learning disability;
- speech or language impairment;
- traumatic brain injury; or
- visual impairment (including blindness from birth).
The ARD committee must make the eligibility determination within 30 calendar days from the date of completion of the initial evaluation report.
-
Acronym List
ARD - Admission, Review & Dismissal
APE - Adapted Physical Education
ASD - Autism Spectrum Disorder
AT - Assistive Technology
BIP - Behavior Intervention Plan
CM - Content Mastery
ED - Emotional Disturbance
ESY - Extended School Year
FA - Functional Academics
FAPE - Free & Appropriate Public Education
FBA - Functional Behavior Assessment
FERPA - Family Educational Rights & Privacy Act
FIE - Full Individual Evaluation
GT - Gifted and Talented
ID - Intellectual Disability
IDEA - Individuals with Disabilities Education Act
IEP - Individualized Education Program
IHPT - In-Home/Parent Training
ITP - Individual Transition Plan
LD - Learning Disability
LRE - Least Restrictive Environment
LSC - Life Skills Class
LSSP - Licensed Specialist in School Psychology
OHI - Other Health Impairment
OT - Occupational Therapy
PLAAFP - Present Levels of Academic Achievement & Functional Performance
PT - Physical Therapy
RTI - Response to Intervention
SBS - Specialized Behavior Support
SI - Speech Impairment
SLP - Speech Language Pathologist
TEA - Texas Education Agency
TEKS - Texas Essential Knowledge & Skills
-
Procedural Safeguards
-
ARD Guide
-
Instructional Services
Leadership Prep School believes in educating students in the least restrictive environment. General education curriculum is the foundation for all instructional programs. The Full and Individual Evaluation, along with current information regarding present levels of academic achievement and functional performance form the basis for decision-making by the Admission Review and Dismissal (ARD/IEP) Committee who determine specific services needed on an individual basis.
A full continuum of instructional and related services is available to eligible students, with initial consideration given to provision of services in the general education classroom to the greatest extent possible. Students spend varying amounts of time in general education and special education settings, depending upon their specific needs. Special education instructional services are available on every campus, as well as, district-wide instructional / related services. Campus services may include full-time placement in a general education classroom and/or pull-out services in a special education classroom. Services are individually determined for each student based on instructional environments that will ensure educational benefit.
-
Related Services
Assistive Technology
Assistive technology (AT) is any item, piece of equipment, software or product system that is used to increase, maintain or improve the functional capabilities of individuals with disabilities. AT provides access to curriculum, allows for independence and enables students to actively participate in their education. AT may include:
-
Low tech to high tech communication systems
-
Computer technologies, such as access switches, keyboards and specialized software
-
FM systems for students in special education
The ARD committee may request an evaluation from the Assistive Technology Team in order to determine if a student needs a specialized device/equipment in order to access his/her curriculum.
Occupational Therapy
Educationally based occupational is provided, as a related service, to enhance the special education student's ability to adapt to and physically function within an educational environment.
The role of the occupational therapist is to facilitate a student's functioning in the school setting. The goal of educationally relevant therapy is to minimize the effects of the student's disability on his or her ability to participate in the educational process.
The OT therapist observes the student's functional skills and offers strategies to promote functional independence within the individualized educational program (IEP). In the school setting, educational objectives hold primary position while therapeutic activities are undertaken to support the educational objectives. Services are generally consultative in nature with implementation of the therapist's recommendations by the teacher, assistant, or parent.
OT services will be provided in the least restrictive environment (LRE), which generally means the classroom. By providing services in the classroom the therapist offers strategies needed for the student's daily activities with active teacher/assistant involvement. These strategies may include handling techniques, classroom modifications, school related self-care skills, fine motor skill development, sensory supports and/or adaptive equipment.
Links
Parent and In-Home Training
Parent and In-Home Training needs will be identified by the ARD committee.
Physical Therapy
Educationally based (school-based) physical therapy, provided as a related service, should be directed towards achievement of the functional tasks required to participate and benefit from special education placement. School-based physical therapy is provided to minimize the effects of the student’s disability on his or her ability to participate in the educational process. The physical therapist evaluates the student’s functional skills and collaborates with school staff to develop an appropriate IEP. The role of the physical therapist is to enhance the student’s ability to fully access and be successful in the learning environment. Services can be direct and/ or consultative in nature with implementation of the therapist’s recommendations by the teacher, assistant, or parent. PT services will be provided in the least restrictive environment (LRE). By providing services in the child’s naturally occurring educational setting, the therapist is able to offer strategies needed for the student’s daily activities with active teacher/ assistant involvement.
Links
Psychological Services
Psychological Services are provided by Licensed Specialists in School Psychology (LSSPs). LSSPs are uniquely qualified members of school teams that support students' ability to learn and teachers' ability to teach. They apply expertise in mental health, learning, and behavior to help children and youth succeed academically, socially, behaviorally, and emotionally. LSSPs partner with families, teachers, school administrators, and other professionals to create safe, healthy, and supportive learning environments that strengthen connections between home, school, and the community (NASP). Specific psychological services are provided when prerequisites have been met. Services include general and special education consultation, special education evaluation, and special education indirect and direct counseling services.
-
-
Transition
Transition is an important component to help students of all ages with disabilities succeed in school. Whether students are transitioning from grade to grade, from early childhood programs to elementary school, elementary to middle school, middle to high school, or high school to college or employment, the special education team at LPS is ready to support our students.Transition is a process of a coordinated set of activities that includes instruction, related services, community experiences, the development of employment and other post-school adult living objectives, and when appropriate, acquisition of daily living skills and functional vocational evaluation.For additional help/information on transition services at LPS, please contact Danelle Standifer, Transition Specialist









